|
A Country with 60 Years of Peace and a Nation with 60 Years of Struggle
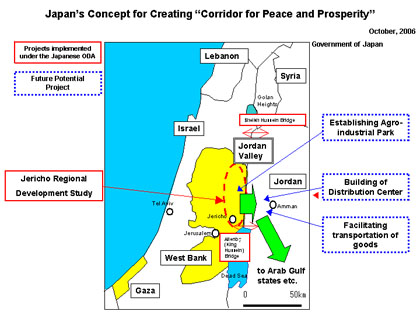
On July 2, Mr. Masahiko Koumura, Japan's Minister for Foreign Affairs hosted the third ministerial-level meeting of the Four-Party Consultative Unit for the “Corridor for Peace and Prosperity”. The meeting was attended by representatives of Palestine, Israel, and Jordan: Dr. Samir Abdullah, Minister of Planning of the Palestinian Authority, Mr. Gideon Ezra, Minister of Environment Protection of Israel, and Mr. Saladin Al-Bashir, Foreign Minister of Jordan. Minister Koumura declared his aim was to promote Japan’s support for co-existence and co-prosperity between Israel and Palestine by stabilizing the Palestinian economy. The meeting was focused on establishing the site of the planned Agro-Industrial Park in the West Bank and facilitating the transportation of goods.
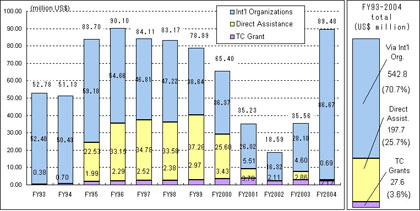
According to the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the four parties reconfirmed their commitment towards the project as they recognized the urgent necessity for the propulsion of the peace process. Access to water and borders for exporting goods can be accomplished only through cooperation of the stockholding countries and this urges those countries' commitment towards peace. This concept is expected to improve employment opportunities and to bring hope for the people in the regions of Palestine, Jordan and Israel. The action plan is slated to begin as soon as the beginning of 2009. The meeting ended with confirming the next technical-level meeting in autumn, 2008 which will discuss the technical issues in detail. Japan and the Arab nations have also been strengthening their relationships by addressing various issues. Japan actively supports a Palestinian self-sustaining economy by assisting to establish industries and transportation in addition to helping improve the social status of individuals by humanitarian assistance such as providing food and medication through international organizations. Japan has been one of the largest donors to Palestinians following the United States and the EU after the Oslo Accords were signed in 1993. Japan's contribution to the assistance of the Palestinians since then has amounted to about $767 million. Since the outbreak of the Intifada in September 2000, Japan provided almost $190 million of assistance with emphasis on humanitarian relief. In addition, during the visit of President Mahmoud Abbas to Japan in May 2005, Japan announced its intention to assist by about $100 million in the immediate future.
Points of Japan's Contributions to the Palestinians
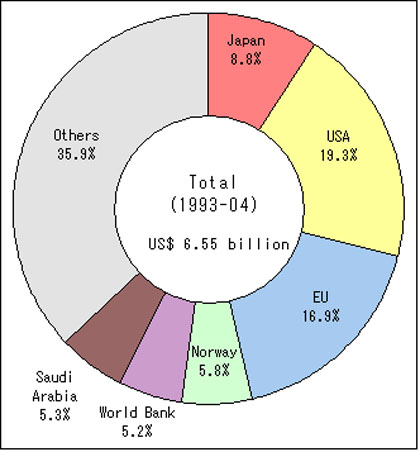
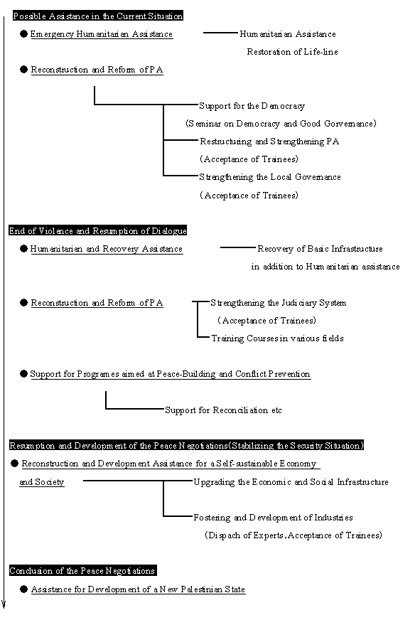
Major Donors' Assistance to the Palestinians (Excluding contributions to UNRWA) Regarding Japan's involvement in Palestinian affairs, what are Palestinian expectations? The head of the Japanese representative office to the Palestinian Authority in Ramallah, Mr. Tetsushi Kondo generously responded to the question: “After what the US did to the people in Iraq, Palestinians are probably wishing Japan will take over the role of the US, which is currently the largest donor to Palestinians.” Japan’s support is usually reflected in the local people’s reaction towards the Japanese people especially in a city like Jericho, where Japan has completed several projects such as building the Jericho New Hospital and repairing the Jericho-Taybeh Road. Mr. Kondo added that there are grass-roots NGO organizations at the local level that are actively interacting with Palestinian youth and adults to assist them with creative activities and health care such as JICA, which has created a Maternal and Child Health(MCH) Handbook, the first of its kind available in Arabic-speaking countries; the Campaign for the Children of Palestine, which established a school for the deaf in Gaza and offered dental treatment to Palestinian youth; the Japan-Palestine Medical Association, which provides medicine and treatment, and the Japanese International Volunteer Center, which offers speech and music therapy for children of trauma. Japan is one of the few countries that show its appreciation for peace in their constitution. After several wars, Japan finally took its first step towards peace in 1947 immediately after WWII and added Article 9 to their constitution: “Article 9 in officially translated English: Aspiring sincerely to an international peace based on justice and order, the Japanese people forever renounce war as a sovereign right of the nation and the threat or use of force as means of settling international disputes. (2) In order to accomplish the aim of the preceding paragraph, land, sea, and air forces, as well as other war” (Article 9 of the Constitution of Japan, May 3, 1947) Adding Article 9 to their constitution was the result of Japan’s continuous state of war and massive destruction by the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. After enduring countless wars, the Japanese eventually recognized the importance of peace. The irony is that 60 years ago, which marked the end of WWII, was the beginning of a peaceful life for the Japanese while it meant disaster and catastrophe for the Palestinians. As a peaceful country that has a history of pain, Japan can perhaps take the initiative to promote a peaceful solution in the Middle East. Road-map for Japan's Assistance to Palestinians (Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan)
Funding for Palestinians from the Japanese government between 2005 and 2008
http://www.miftah.org |